| [1] Cole CD, McCall TD, Schmidt MH, et al. Comparison of low back fusion techniques: transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) or posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) approaches. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2009;2(2):118-126. [2] Ploumis A, Wu C, Fischer G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of anterior lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(2):120-125.[3] 王广积,谭军贾,连顺侯,等.后路椎体植骨融合椎弓根钉内固定治疗腰椎滑脱症[J].颈腰痛杂志,2002,23(1):34-36.[4] Booth KC, Bridwell KH, Eisenberg BA, et al. Minimum 5-year results of degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and instrumented posterior fusion. Spine. 1999;24(16):1721-1727.[5] Tay BB, Berven S. Indications, techniques, and complications of lumbar interbody fusion. Semin Neurol. 2002;22(2):221-230.[6] 陈文治,葛鸿庆,王君鳌,等. USS系统后路固定加椎间植骨治疗腰椎节滑脱症[J].中医正骨, 2004,16(10):29-30.[7] Sidhu KS, Herkowitz HN. Spinal instrumentation in the management of degenerative disorders of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(335):39-53.[8] Rantanen J, Hurme M, Falck B, et al. The lumbar multifidus muscle five years after surgery for a lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Spine. 1993;18(5):568-574.[9] Toyone T, Takahashi K, Kitahara H, et al. Visualisation of symptomatic nerve roots. Prospective study of contrast-enhanced MRI in patients with lumbar disc herniation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75(4):529-533.[10] 刘云鹏,刘沂.骨与关节损伤和疾病的诊断分类及功能评定标准[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2002:5-6.[11] 王华东,侯树勋.腰椎节段性不稳的治疗与研究进展[J].继续医学教育,2005,19(7):45-47.[12] 王亮,朱冬承,戈兵,等.单侧钉棒固定单枚Cage融合治疗腰椎间盘突出合并腰椎不稳症[J].颈腰痛杂志,2011,32(05):357-359.[13] 何二兴,曹燕明,范子文.经神经根孔入路腰椎融合术治疗腰椎间盘突出伴腰椎不稳[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2005,9(4):299-301. [14] 傅晨,张功林,杨成勇,等.内固定加植骨融合治疗腰椎间盘突出合并腰椎失稳[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(10):755-756.[15] 袁永集.腰椎间盘突出症伴腰椎不稳56 例诊治分析[J].中国厂矿医学,2006,19(5):411-412.[16] 曹刚.椎弓根内固定加植骨治疗腰椎不稳并椎间盘突出症[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2009,30(6):514-515.[17] Styf JR, Willén J. The effects of external compression by three different retractors on pressure in the erector spine muscles during and after posterior lumbar spine surgery in humans. Spine. 1998;23(3):354-358.[18] Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang ZF, et al. Minimally invasive or open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion as revision surgery for patients previously treated by open discectomy and decompression of the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(4):623-628. [19] 易伟宏,黄曹,陈开林,等.内窥镜下手术治疗腰椎间盘退变性疾病的并发症[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(12):916-920.[20] 陈远武,易伟宏,刘春利,等.METR_X内窥镜辅助X-Tube下减压、融合、内固定治疗腰椎退变性疾病[J].临床骨科杂志,2009,12(3):254-256.[21] 孟志斌,李俊,李洪潮,等.X-TUBE内镜下椎弓根钉内固定治疗退行性腰椎管狭窄伴腰椎滑脱的近期临床观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2008,29(2):124-127.[22] Glaser J, Stanley M, Sayre H, et al. A 10-year follow-up evaluation of lumbar spine fusion with pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 2003;28(13):1390-1395.[23] Lin PM. A technical modification of Cloward's posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurgery. 1977;1(2):118-124.[24] Guan HG, Wang G, Huo ZM, et al. Minimally invasive surgical treatment for lumbar degenerative disease with IsoC-3D navigation under Mast Quadrant system. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(6):451-454.[25] Haji FA, Cenic A, Crevier L, et al. Minimally invasive approach for the resection of spinal neoplasm. Spine. 2011;36(15):E1018-1026. [26] Liu T, Zhou Y, Wang J, et al. Clinical efficacy of three different minimally invasive procedures for far lateral lumbar disc herniation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(6):1082-1088.[27] Logroscino CA, Proietti L, Pola E, et al. A minimally invasive posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spine instabilities. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 1:S41-45. [28] 韩建龙,左金良,黄波,等.腰椎间盘突出症不同术式的远期疗效比较[J].实用骨科杂志,2006,12(1):12-14.[29] Chekhonatski? AA, Chekhonatskaia ML, Sharova EV, et al. Complex approach to the treatment of the diskal hernia of lumbosacral spine. Voen Med Zh. 2010;331(8):25-28.[30] Kasai Y, Inaba T, Kato T, et al. Biomechanical study of the lumbar spine using a unilateral pedicle screw fixation system. J Clin Neurosci. 2010;17(3):364-367. [31] Ozgur BM, Yoo K, Rodriguez G, et al. Minimally-invasive technique for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF). Eur Spine J. 2005;14(9):887-894. [32] North RB, Campbell JN, James CS, et al. Failed back surgery syndrome: 5-year follow-up in 102 patients undergoing repeated operation. Neurosurgery. 1991;28(5):685-690. |
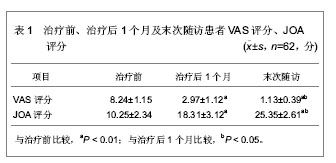
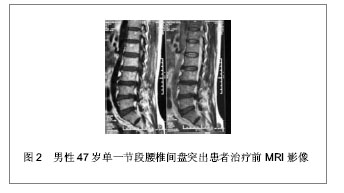
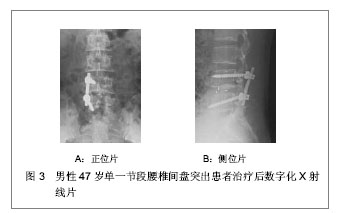
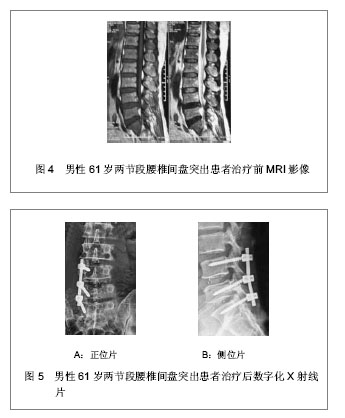
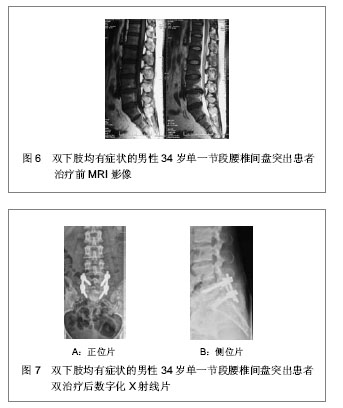
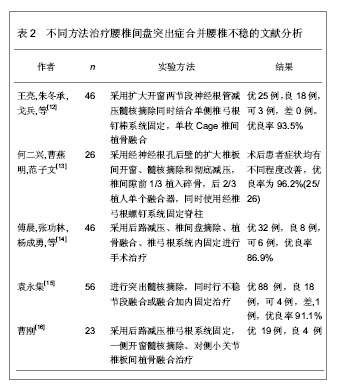
.jpg)